Register now or log in to join your professional community.

Financial roadmap planning is priority.
It apply for startup and also on growing corporate, without it. The question to ask is What is their company KPI.
For startup, by working on financial roadmap, you gets the valuation of the company, also knows the estimation share prices and KPI to achieve.
Once you did that, run the business for at least a year or 6 monts. The re-check if the reality of the market can match up with your planning. If it showed on track, then you can assure that your company valution is on track. This can be shown to upcoming investor bout your company valuation. Its useful when you want to apply for fund raising.
There are others way evaluate a company, such as scorecard method, venture capital method, checklist method & more.
It depends on what method you apply. However, if you the company business can grow to international market. Strongly suggest venture capital method, which required Financial Roadmap. This is the method that all the Tech company using.

I agree with Mr.Hong Son Tay

Thanks for inviting , so far i agree with expert reply

agree with the experts........

Although there are several formulas you can use, there are no black-and-white answers on valuation techniques.
It’s important to conduct your own research, then get independent advice from a business valuer or broker. Here are four of the most commonly used valuation methods:

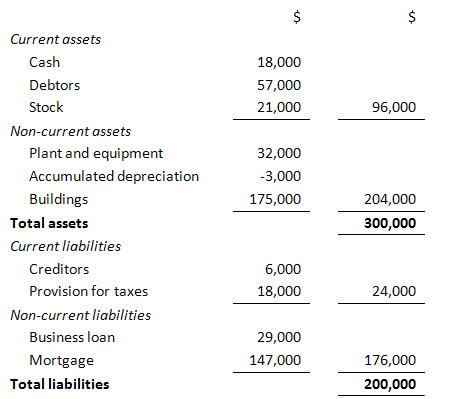
How it works
Example
What about goodwill?
How it works
Example
David is looking at buying a bakery business with average net profits of $100,000 per annum after adjustments. David wants an annual rate of return of 20 per cent. The capitalised earnings valuation is:
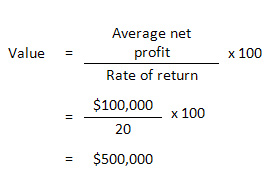

through chances various,through all vicissitudes ,we make our way....





Do you need help in adding the right keywords to your CV? Let our CV writing experts help you.